
A drone, in its simplest form, is an aircraft that operates without a human pilot onboard. Also known as an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), drones can be controlled remotely by a human operator or fly autonomously using sophisticated onboard computer systems. These versatile flying machines have revolutionized various industries, with the global drone market experiencing significant growth in recent years, and they continue to evolve rapidly as technology advances.
The word “drone” has several meanings. In aviation, it refers to unmanned aircraft, the focus of this article. However, “drone” can also mean a male bee whose main role is to mate with the queen, or colloquially, a person who does tedious or monotonous work. In this article, we explore the technological marvels of drones that fly through the skies.
How to Pronounce “Drone”: The word drone is pronounced /droʊn/, rhyming with “known” and “tone”.
Drone Meaning (Simple Explanation)
At its core, a drone is a flying robot that can be remotely controlled or programmed to fly autonomously. Think of it as a flying computer with propellers, sensors, and cameras that can perform tasks that would be difficult, dangerous, or impossible for humans to do directly. In recent years, commercial drones have generated thousands of new jobs in the U.S., and there are now over 1.2 million commercial drones in Europe.
Definition of Drone for Kids: A drone is like a small flying machine or robot that can fly without a person inside it. People can control it from the ground, or it can fly by itself using computers and sensors.
Drone vs. UAV vs. UAS: Clearing Up Common Confusion
While these terms are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences:
- Drone: The common term for any unmanned aircraft, originally derived from military terminology.
- UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle): The technical term specifically referring to the aircraft itself.
- UAS (Unmanned Aircraft System): A more comprehensive term that includes the drone, controller, communication systems, and other components necessary for operation.
Brief History & Evolution of Drone Technology
Drones have evolved dramatically since their early military applications:
- 1910s-1930s: Early unmanned aircraft developed primarily for military target practice.
- 1940s-1960s: Military reconnaissance drones emerge during the Cold War.
- 1980s-1990s: Advanced military UAV development accelerates.
- 2000s-2010s: Consumer drones become available, with companies like DJI leading the market revolution. DJI commands an estimated 70-80% of the global consumer drone market.
- 2010s-2020s: Explosion in commercial applications and technological capabilities.
- 2020s-Present: Integration of AI, advanced autonomy, and specialized industry solutions, with businesses and government agencies investing heavily in drones and drone services.
From their humble beginnings as remote-controlled aircraft used for target practice, drones have transformed into sophisticated machines that can change the dynamics of both warfare and civilian life. The integration of artificial intelligence and advanced autonomy has propelled these unmanned vehicles into becoming vital assets across various sectors.
Types of Drones: Understanding Categories and Classifications
1. Types Based on Design
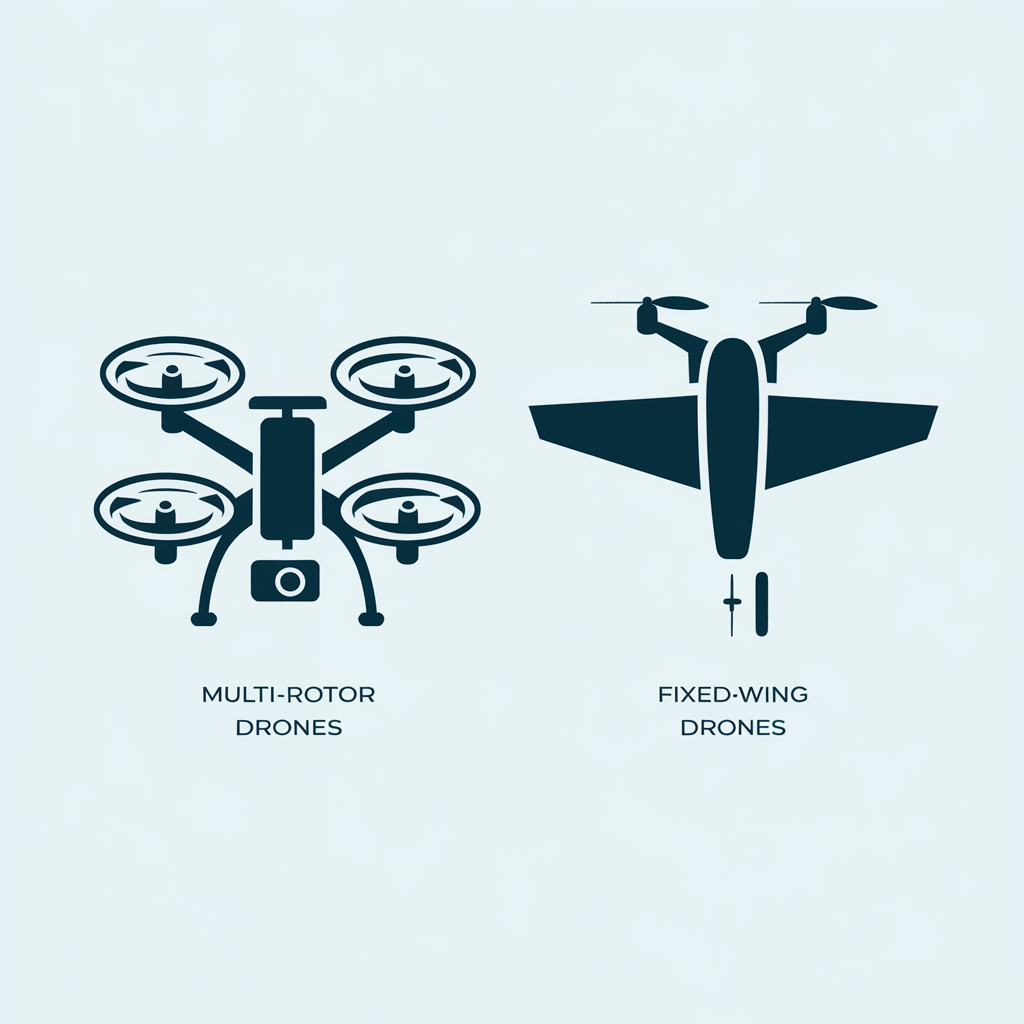
Comparison of Drone Types Based on Design
| Drone Type | Pros | Cons | Common Uses |
| Multi-Rotor Drones | – Excellent maneuverability and hovering capability- Simple design and easier to manufacture- Lower cost entry point for beginners- Vertical take-off and landing | – Limited flight time (typically 20-40 minutes in 2025)- Lower speed efficiency- Less efficient in forward flight- Limited payload capacity compared to other designs | – Aerial photography and videography- Site inspections- Recreational flying- Short-range delivery services- Surveillance in confined spaces |
| Fixed-Wing Drones | – Extended flight time (several hours possible)- Efficient aerodynamics for faster speeds- Capability to cover larger areas- Better energy efficiency- Higher payload capacity for size | – Cannot hover in place- Require runway or launching mechanism- More complex to operate for beginners- Typically higher initial cost | – Large-scale mapping and surveying |
As of 2025, the number of recreational drones in use has increased significantly. Battery technology advancements have extended typical drone flight times by 30-50% since 2020. Consumer drones in 2025 typically have ranges of 5-15 km, while professional models can reach 30+ km. The drone delivery market is projected to grow substantially in the coming years.






